Editorial policy
Editorial approach
POSTULADOS SOCIOJURIDICA JOURNAL, is an electronic-scientific publication, published every six months, edited by the Department of Law and Political Science of the Universidad Francisco de Paula Santander Seccional Ocaña, which aims to promote the dissemination of theoretical, critical and reflective studies in the area of Social Sciences, in the discipline of Law and thematic lines related to: Local and Regional Development, Public Law, Constitutional Law, Private Law, Human Rights, Criminal Law, Labor Law, International Law and socio-legal, according to the documentary typologies. From the legal and socio-legal sciences at the national, Latin American, and international level for possible publication of original articles, research, review and/or reflection, which may be submitted in Spanish, English or Portuguese, without processing or publication fees.
Target audience
The journal is addressed to all graduate students, researchers and professionals of Law and Social Sciences. Each issue of the journal has a diverse character, without prejudice to edit when deemed appropriate single-thematic issues. The submission of a manuscript does not imply its publication, which should be subject to the guidelines for authors of the journal and the policies of the Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE), for its subsequent evaluation by peer reviewers under the double-blind arbitration system.
1.1. Documentary typology
POSTULADOS Sociojuridica Journal publishes research articles, which correspond to one of the following typologies.
RESEARCH RESULT ARTICLE: A document that presents in detail the original results of a research project completed or in progress.
REFLECTION ARTICLE: A document in which the results of a completed research project are presented from a critical, analytical, and interpretative perspective carried out by the author, using original sources.
REVIEW ARTICLE: It is the result of a research process, which is characterized by a rigorous bibliographic review comprising more than 50 references. This typology presents a state of the art on a specific subject, in which the advances and new trends on the subject under study are evidenced.
1.2 Margins and spacing:
For the preparation of the document, the article should be in letter size (21.59 x 27.94), adjust the 4 margins to 2.54 cm. Line spacing (2.0) should be used. The body of the paper should be in two columns, with a spacing of 0.75 cm between columns.
Paragraphs should be justified, the first paragraph after each section or subsection should not be indented; subsequent paragraphs should be indented by 0.5 cm. The distance between paragraphs is one line.
1.3. Titles
Section title: Times New Roma font, size 12, bold. It should be spaced one line before the paragraph and without space after the section heading. The title should not contain a period.
Section subtitle: Times New Roman font, size 12, no bold. It should be spaced one line before the paragraph and without space after the section heading.
Sub-subtitle: Times New Roman font, size 12, non-bold and in italics. It must end with a period (period) and run in the text of the paragraph.
1.4 Numbering
Sections should be numbered with a period following the number and then separated by a single space. Ex:
Title: 1. Postulates
Sections should be numbered 1., 2., 3., etc.
Sub-sections should be numbered 2.1., 2.2., 2.3., etc.
Subsubsections should be numbered 2.3.1., 2.3.2., etc.
1.5 Equations
Equations within an article must be numbered in order of appearance. The equation number is enclosed in parentheses and adjusted to the right side of the column while the equation is centered.
Equations should be cited within the text of the paper and their location should be close to the citation. The equation should be written using the MathType equation editor, without bold, size 12 and in italics.
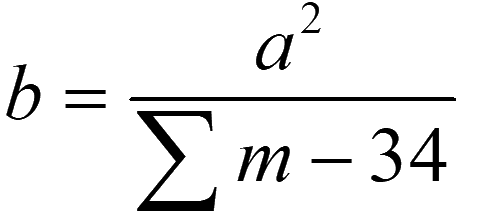 (1)
(1)
1.6 Figures
All illustrations, graphs, drawings, images, photographs, etc., should be cited as figures. Figures are numbered in order of appearance in the text of the article with Arabic numerals. All figures should be cited in the text and their location should be close to the citation.
Figure caption. All figures must have a caption. The caption should be short and should not appear as a title. The caption should be adjusted to the width of the figure, for wider figures, centered on the width of the figure, or, for narrow figures with wider captions, should extend beyond the width of the figure. The word Figure, the consecutive number (both in bold) and the caption should be below the figure by a distance of 6 points, in Times New Roman font size 10. If the figure has parts, include identifying labels in the assembly. The identifiers will be (a), (b). The figures must be embedded in the document with a resolution of 300 dpi, they should not be attached separately. If the figure is taken from another source, the corresponding information should be included at the bottom, with the phrase Source: xxxxxxx. In this version of the APA standard, as well as tables, figures may contain 3 types of notes if general, specific and probability notes are necessary.
It is important to emphasize that the figure must be inserted inside a table, without visible borders. Example:
Figure 2
Additional poverty attributable to Covid-19 in 2020.
Note. The figure shows the projected increase in 2020 based on two scenarios (baseline and aggravated). (Soler Lecha, 2020)
1.7 Tables
Place tables and figures at the top or bottom of columns; avoid placing them in the middle of columns.
Tables should be referenced within the document as (Table 1), numbered consecutively using Arabic numerals and should always have a title that concisely but completely indicates their contents. The title and content of the table should be in Times New Roman font size 10, aligned to the left. The title should be placed before the inclusion of the table.
The word Table, the consecutive number (both in bold), the content of the table should not be in bold. All tables must be cited in the text and their location must be close to the citation. Images should not be attached as tables, they should all be done in Word (see table 1). If the table is taken from another source, the corresponding information should be included at the bottom, with the phrase Source: xxxxxxx.
Tables should have only horizontal and not vertical rules, i.e., only horizontal lines should be used at the top or bottom of the table as shown in the example in figure 1, only, if necessary, intermediate lines can be added, taking into account the organization of the information and its readability.
Figure1
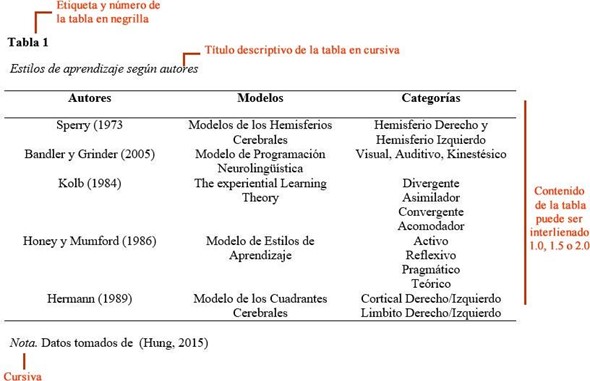 Example of table presentation
Example of table presentation
As can be seen in the previous example, tables under the APA NORM model do not have vertical margins.
Sometimes the tables must be accompanied by explanatory texts defined as notes, these are classified as: general note, specific note and probability note, when the table contains general note, at the end of the same is located a period followed by the source, if it also contains specific or probability notes are located after a full stop on different lines.
1.8 Notation and Symbols
When defining terms, variables, constants, parameters, symbols, use those that have a generalized or standardized use. This allows the reader to have a more agile approach to the topics covered in the article. Indeed, when working with general variables it is common to use the letters x, y or z to identify them as they appear, in italics.
1.9 Acronyms or abbreviations
Articles may use acronyms or abbreviations, but they must be defined the first time they are mentioned in the text, even if they have already been defined in the abstract.
Some examples might be "... unidentified flying object or UFO...", "... CPI or Consumer Price Index", "... the OAS (Organization of American States) ...". Given the nature of the articles, some acronyms or abbreviations come from English; in this case the acronym must be defined in both Spanish and English. For example, the acronym HTML is an acronym of English words and could be defined as "... text markup language or HTML (hypertextmarkup language) ...". Do not translate widely used acronyms. For example, use CPU (Central Processing Unit) and not CPU (Central Processing Unit). Acronyms containing periods should be written without spaces, i.e., "C.N.T." and not "C. N. T."
1.10 Footnotes
Footnotes should be kept to a minimum and their use is recommended to clarify concepts, not terms, remembering that the reader has knowledge of the subject, they should generally not be used. Use superscript numbers in the text to indicate reference to a particular footnote.
1.11 Methodology
It should begin by describing the complete experimental design and the theoretical procedures used.
The premises and assumptions made must be explicitly stated and the choice of methods must be justified in those situations where other reasonable alternatives exist.
The description of the methods must be sufficiently detailed to allow any experienced researcher to reproduce it, this description must follow a logical order so that the reader can understand how the described manipulation fits the experimental design. The information should describe the following:
The design of the experiment or investigation.
The sample.
The restrictions or limitations.
Techniques.
The procedures.
Materials.
Variables.
Statistical treatment.
1.12 Results
Include only data and information related to the topic. They will be presented in a sequence that supports the hypothesis or answers the question posed in the introduction. Frequently the results are presented through tables and figures. The information to be included is:
Information to locate the figures.
Information to present the most important contributions.
Information to comment on the results.
In some cases, discussions are presented with the results or in a separate section, where the implications of the results presented are evaluated and interpreted with special reference to the initial hypothesis. This section should begin with a clear sentence indicating whether the initial hypothesis can be maintained.
1.13 Conclusions
In this section the conclusions of the research are mentioned very succinctly, as a reminder of the most important ideas. The conclusions do not include citations of bibliographical references.
1.14 Acknowledgments
In this section, the author expresses his gratitude to an institution, in addition to the name of the project that originated the research.
1.5 References
References should be cited within the text of the article. The minimum number of references should be 12 references with a maximum of 5 years prior. References should be in APA STANDARD, the author should be cited in the text and additionally added in the list of references. Each reference usually contains the following elements: author, year of publication, title and publication data.
References should be placed with French indentation, that is, the first line should be aligned with the left margin and the following ones at 1.27 cm and the line spacing should be double (2.0).
Scientific journal references
The table below describes the elements of a complete reference for a scientific journal, in the case of a non-electronic journal you should omit the URL information.
Elements of a scientific journal reference
|
Información básica |
|
Información de la fuente |
||||
|
Autor |
Fecha |
Título del artículo |
Título de la revista |
Volumen (número) |
Número de página (s) |
DOI o URL |
|
Iñaki, J. A |
(2014) |
Universidad, ciudadanía y TIC |
Análisis |
46(85) |
345-365 |
https://www.redalyc .org... |
Example:
Iñaki, J. A (2014). Universidad, ciudadanía y TIC. Análisis, 46(85), 345-365. https://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=515551536009
Many newspapers publish articles without page or article numbers. Omit these elements from the reference if they are not present in the cited work. For a printed version, no URL is included..
Elements of a newspaper reference
|
Información básica |
|
Información de la fuente |
|||
|
Autor |
Fecha |
Título del artículo |
Título del periódico |
Número de página (s) o sección |
DOI o URL |
|
Prats, J. A |
(2014, 28 de Octubre ) |
Mujer y Universitaria |
La vanguardía |
36-53 |
ttps://www.lavanguardia.co m/opinion... |
Example online versión
Prats, J. (2012, 28 de Octubre). Mujer y universitaria. La vanguardía. https://www.lavanguardia.com/opinion/temas-de-debate/20121028/54353571405/mujer- y-universitaria.html?page=1
Example versión impresa
Prats, J. (2012, 28 de Octubre). Mujer y universitaria. La vanguardía.C1
Books
The table below describes the elements of a complete reference for a book, in the case of a printed book you should omit the URL information.
Elements of a book reference
|
Información básica |
|
Información de la fuente |
|||||
|
Autor |
Fecha |
Título del libro |
Edición |
Editorial |
DOI o URL |
||
|
Hernández Sampieri, R |
(2014) |
Metodología de la Investigación |
(6ª ed.) |
Mac Graw Hill |
|||
Exampl
Hernández Sampieri , R. (2014).
Metodología de la Investigación (6ª ed.). Mac Graw Hill.http://observatorio.epacartagena.gov.co/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/metodologia-de-la- investigacion-sexta-edicion.compressed.pdf.
References from a book chapter
This type of reference is only used when the book consists of several chapters that are written by different authors, if the book is written entirely by the same author or group of authors a normal book reference is used, in the case of a printed book the URL information should be omitted.
Elements of a book chapter reference
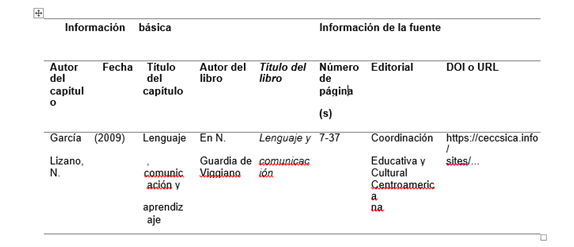
Example:
GarcíaLizano,N.(2009).LENGUAJE,COMUNICACIÓNYAPRENDIZAJE.EnN.Guardia de Viggiano, Lenguaje y comunicación. (pp. 7-37). Coordinación Educativa y Cultural Centroamericana. https://ceccsica.info/sites/default/files/content/Volumen_25.pdf.
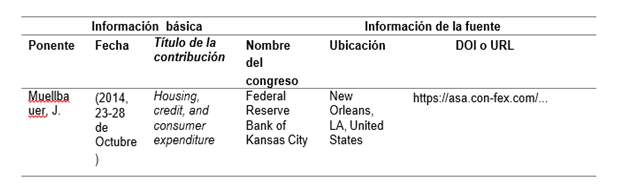
References of a congress
The following table presents the information for referencing a paper in a congress. If you need to reference symposia, please take into account the information presented here and consult the publications manual in the seventh edition to complement the fields.
Elements of a book chapter reference

Example:
Muellbauer, J. (2014, 23-28 de Octubre). Housing, credit, and consumer expenditure. Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City, New Orleans, LA, United States. https://asa.con-fex.com/...
References of dissertations, undergraduate and graduate theses
Dissertations and theses can be retrieved from subscription databases, institutional archives and personal web pages.
This type of references applies to any type of thesis, locate within the square brackets the type as appropriate, example 1 shows a master's thesis and example 2 shows an undergraduate thesis.
Dissertation, undergraduate and graduate thesis reference elements
|
Información básica |
|
Información de la fuente |
|||
|
Autor |
Fecha |
Título de la disertación/ tesis |
Nombre de la institución |
Nombre de la base de datos o archivo |
DOI o URL |
|
Adams, R.J |
(2020) |
Housing, credit, and consumer expenditure |
Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City |
New Orleans, LA, United States |
https://asa.con-fex.com/... |
Example1:
Adams, R.J. (2020). Bulding a foundation for evaluation of education and continuing education.[Tesis de maestría, University of Virginia]. New Orleans, LA, United Stateshttp://www.ohiolink.edu/etd/
Example2:
Lobo Díaz, O.I. (2016). Design of an architecture based on "SDN" (Software Defined Networking) technology for the networking and telecommunications laboratory of the Universidad Francisco de Paula Santander Ocaña. [Undergraduate thesis, Universidad Francisco de Paula Santander Ocaña].UFPSO Institutional Repository.http://repositorio.ufpso.edu.co/handle/123456789/1002
Audiovisual media references
Audiovisual media can have both visual and audio components. The first column of Table 11 shows the media categories to be taken into account in this type of references.
Type of author according to type of media
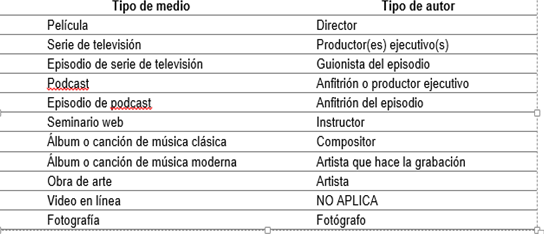
Note. Adapted from the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association 7th Edition, Header Levels, p.347 (2021).
Psychological Association 7th Edition, Header Levels, p.347 (2021)
Table X should be consulted to identify what information to include in the parenthesis after the author with which the corresponding author type will be established.
In the first Example, an online video is referenced for this type of media, this information is omitted (it is the only one where it is omitted) in the second, which corresponds to a television series, the author type information is executive producer, this information is placed before the parenthesis with the date and separated with a period.
Type of author by media type
Example:
Paulo Freire Educational Center (2016). Virtual Education, Myths and Realities [Online video]..
Instituto Freire. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=A-trAQNpjEI
CCardona, M. (Executive producer) (2020). Quien mató a Sara [Television series]. 1111films.tv. HBO.https://www.seriestv/watch?v=A-trAQN
Websites and web pages
Use the pages and websites source type if there is no other type of reference that fits and the work has no top or global publication by Example a scientific journal other than the website itself. If you cite multiple pages from a website, create a reference for each. (American Psychological Association, 2021)
Type of author by media type

When the author and site name is the same, omit the site name from the source element.
The date depending on the site or web page consulted, may take one of the following forms:
Year only Year, day and month Year and month.
The copyright registration date from the footer of the page or website should not be used because this date may not indicate when the site content was published.
If a note indicates the "last updated" date use that date if it applies to the content you are citing.
If no separate publication date is given for the work on the web page, treat the work as if it were undated.
Example
Mineducación.(2020,21 deMayo).SistemaEducativoColombiano.https://www.mineducacion.gov.co
In the previous example, since the author is the same name of the site, the latter was omitted in the reference..
Legal References
The structure of the legal references was determined based on a review of the document 'Guide for the citation of legal sources in Colombia based on the criteria of the APA 7th edition style'.
The following is the basic structure, adjust the referencing according to your need depending on the type of legal source, based on the Examples shown below.

Examples:
Constitution
National Constituent Assembly (1991). Political Constitution of Colombia of 1991.
Constitutional Gazette 116 of July 20, 1991.
http://www.secretariasenado.gov.co/senado/basedoc/constitucion_politica_1991.html
Laws
Congress of the Republic of Colombia (2006). Law 1098 of 2006. Whereby the Code for Children and Adolescents is enacted. Official Gazette 46.446 of November 8, 2006. http://www.secretariasenado.gov.co/senado/basedoc/ley_1098_2006.htm
Sentences
Constitutional Court of Colombia. Plenary Chamber (1993). Decision C-411. Presiding Judge Carlos Gaviria Díaz. http://www.corteconstitucional.gov.co/relatoria/1993/C-411.htm
Decree
Presidency of the Republic of Colombia (1991). Decree 2700 of 1991. By which the rules of criminal procedure are issued. Official Gazette 40.190 of November 30, 1991. https://normativa.colpensiones.gov.co/colpens/docs/codigo_procedimiento_penal_1991.htm
Resolution
Ministry of Health of the Republic of Colombia (1993). Resolution 8430 of October 04, 1993. By which the scientific, technical and administrative norms for health research are established. https://www.minsalud.gov.co/sites/rid/Lists/BibliotecaDigital/RIDE/DE/DIJ/RESOLUCION8430-DE-1993.PDF
Agreement
National Penitentiary and Prison Institute (1995). Agreement 0011 of October 31, 1995. Whereby the General Regulations to which the internal regulations of the Penitentiary and Prison Establishments shall be subject are issued. http://www.inpec.gov.co/documents/20143/44983/ACU ERDO++11+de+1995+y+ACUERDO+11+AGT06+Mdfca+Acdo+11OCT9.pdf/c46039b6- c163-7197-ef74-83db3da8568d
Directive or circular
Fiscalía General de la Nación. (2017). Directive 002. Whereby general guidelines are established on the investigation of crimes committed against human rights defenders in Colombia.
https://www.fiscalia.gov.co/colombia/wpcontent/uploads/Directiva-002-2017.pdf
Description of item components
Spanish Title
(Maximum number of words 150 characters, only the initial letter must be capitalized, except for proper names, acronyms, or acronyms. It should not contain names of places or specific dates. The types of titles are indicative or informative).
Author data
Names Surname1, Names Surname2, Names Surname,
1 Research group, University or institution, Country, Email, Orcid. Email:
2 Research group, University or institution, Country, Email, Orcid. Email
3 Research Group, University or Institution, Country, Email, Orcid.
Abstract:
This template shows the formal and stylistic aspects that articles submitted to the XXX journal must comply with, providing a brief description of each section and guiding authors in the process of writing their articles. The abstract should have a maximum length of 200 words. It should comply with the structure of an analytical abstract (Background, aim, methodology, results and conclusions) stating what was done, how it was done, the main results and their significance. It should not contain abbreviations, bibliographic references, or unknown characters. If acronyms or abbreviations appear in the abstract, they must be defined. State what was done, how it was done, the main results and their significance. The abstract should be understandable without the need to refer to the rest of the text, figures, or tables of the article. Remember that the summary or abstract is what an interested reader reads first to learn about the content of the article. The font is Times New Roman in 10-point size.
Keywords
Write the keywords separated by comma. Maximum eight (8) words, minimum four (4), sort alphabetically. The font is Times New Roman in 10-point size.
Guidelines
Files should be sent in Microsoft Word format. Figures and tables should be embedded in the document, and should not be sent separately, with a resolution of 300 dpi.
Articles should contain the following structure:
Research articles
Title in English and Spanish
Author information
Abstract in English and Spanish
Keywords in English and Spanish
Introduction
Explanations and rationale (theoretical descriptions and state of the art)
Methodology
Results
Discussion
Conclusion
Reflection articles
Title in English and Spanish
Author information
Abstract in English and Spanish
Keywords in English and Spanish
Introduction
Reflection
Conclusions
Bibliographical references
Acknowledgements
Review Articles
Title in English and Spanish
Author information
Abstract in English and Spanish
Keywords in English and Spanish
Introduction
Methodology
Results and discussion
Conclusions
Bibliographical references (minimum 50)
Acknowledgments
Submission process
The author should submit the manuscript in Word format via the journal's e-mail address. Cover letter and originality:
Transfer of rights act:
Author Data Update Form: Where authors are asked to provide their personal data, academic background and scientific productivity.
Supplementary files:
4. Editorial process
For papers submitted to the journal that pass the first phase of review, the Editorial Committee assigns a minimum of two national and international peer reviewers, under the "double-blind arbitration system" (the identities of authors and peers are not disclosed), who will be responsible for ensuring the relevance, quality and level of contribution of the manuscripts to the field of knowledge. As a result of this exercise, the reviewers issue an opinion with their opinion and recommendations for the improvement of the manuscript.
The reviewers should take into account the following considerations.
They may only accept the review of articles in which they have sufficient knowledge.
Carry out the respective revisions within the established times.
Respect the confidentiality of the information to be published.
Your opinion may not be influenced by commercial considerations.
Their opinions must be objective and constructive.
Once the peer reviewers' opinions have been received, the Editorial Committee will analyze and compile the reviewers' recommendations, which will be sent to the authors with the final decision.
The Editor and Editorial Committee, once it receives the results of the evaluations issued by the juries, will define and communicate to the authors any of the following responses:
Accepted: the paper will be published as it was received and only spelling and style adjustments will be made.
Accepted with minor changes: the paper will be published when the authors comply with and/or support the adjustments suggested by the reviewers; these will be reviewed by the Editorial Committee and/or the peer reviewer (if he/she deems it necessary), who will decide whether they are accepted or not.
Accepted with major changes: the work must be corrected both in content and form according to the suggestions made by the peer reviewers. The new version of the paper will have, once again, the corresponding evaluation by the peers who will determine if the authors followed the respective suggestions.
Note: Due to the evaluation processes of the Postulados Journal, it is not possible to assure the authors of the immediate publication of their work. Ethical considerations
Conflict of interest: Authors declare any conflicts of interest in connection with the submitted article. If any, it is imperative that they identify them and explain their relationship to the submitted work.
Procedure for dealing with inappropriate behavior.
Inform the author or reviewer that a misunderstanding or misconduct has been identified.
Inform the author or reviewer by means of a more robust letter explaining the misconduct and serving as a warning for the future.
Publish an editorial detailing the misconduct.
Send an official letter to the head of the department where the author, reviewer or sponsoring institution belongs.
Formally withdraw the article from the journal.
Responsibilities of the authors
Maintain records and supports of the manuscript data and facilitate access to them in case of request.
Ratify that the manuscript is original, was not submitted or accepted for publication in another journal or media.
Correctly cite the content taken from other sources, in case of coincidence of content with a previous work, the source must be cited.
Obtain the corresponding permission to reproduce any content from other sources.
All studies performed on humans or animals must comply with the relevant laws and requirements.
Declare any possible conflict of interest.
Inform the journal editor or publisher if a significant error is identified in your article.
Support the process of erratum, addenda, corrigenda, or withdrawal of the article, when deemed necessary.
The information and supports used in each article are the direct responsibility of the authors, the Editorial Committee is not responsible for legal situations that may arise in reference to each article.
It is clarified that the submission of the article does NOT guarantee that the authors do not infringe copyright and that the work has not been published elsewhere and is not under evaluation for publication in other print or electronic media.
Responsibilities of reviewersSupport editorial decision-making and help improve the quality of the work to be published through objective review of the manuscript, meeting deadlines.
Maintain the confidentiality of the information provided by the editor or author. Not to retain or copy the manuscript.
Inform the editor of any work, submitted, or published, that is in any way similar to the one under review.
Responsibilities of the Editor and Editorial Committee
Make the final decision to publish an article based on compliance with editorial policies, ethical standards, and the opinion of peer reviewers.
Disclose possible conflicts of interest.
Maintain confidentiality of manuscript information.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution - Noncommercial - 4.0 International License.
Names and email addresses entered in this journal will be used exclusively for the purposes set forth herein and will not be provided to third parties or for use for other purposes.